The Hexagram Structures
A hexagram is a six line totem figure. In traditional texts it is said that the trigrams are doubled to form a hexagram.
The Places: There are six places in each hexagram, each one above the other. They are numbered from one to six. The first place being at the bottom, and the sixth place being at the top.

Each of the places is occupied by a solid or a broken line.

There are 64 possible combinations of solid and broken lines in a six place totem.
These sixty-four hexagrams represent the Book of Changes. The order in which they appear is known as the Sequence of Change.
Primary Trigrams
In every hexagram there are two primary trigrams: one above and one below.
Above ![]() Upper Primary Trigram
Upper Primary Trigram
Below ![]() Lower Primary Trigram
Lower Primary Trigram
It is from the relationship between these two primary trigrams, their attributes, nature symbols and family membership that the primary meaning of the Hexagram and its name are determined.
Occasionally a hexagram gets its name from the picture of the lines themselves or from the structure of the hexagram.
An example would be Splitting Apart:

Each trigram has a relationship to itself and to every other trigram, making in all sixty-four relationships or sixty-four hexagrams. It is the nature of these relationships and their implications that have fascinated and absorbed the minds of great scholars for centuries upon centuries. The meanings of these relationships also appealed to the common person and allowed them to access the teachings and apply it to their lives.
The Upper Primary Trigram relates to the outer (objective) social cultural world around us with all of its challenges.
The Lower Primary Trigram relates to the inner subjective personal world within us and to our personal lives at home.
They reveal outer motivation and integrity. They also reveal inner motivation and integrity. The implications of these inner and outer relationships encompass the various experiences and challenges in life.
Nuclear Trigrams
Within every hexagram there is a hidden or inner theme that adds relevance and direction to the relationships of the primary trigrams.
Upper Nuclear  Lower Nuclear
Lower Nuclear
Within every hexagram there are two nuclear trigrams: an upper nuclear and a lower nuclear trigram, which create a nuclear hexagram. (A theme within the theme.)
These are determined by leaving out the first line at the bottom and the sixth line at the top. The first line is at the beginning and plays a supposed lesser role in the whole hexagram, because it is only starting and not following through. The sixth line is at the top and plays a lesser role in the whole hexagram because it is ending or leaving it.
The nuclear trigrams are determined from the middle four lines.
 Upper Nuclear Trigram
Upper Nuclear Trigram

Lower Nuclear Trigram
The lower nuclear trigram consists of the lines in places 2, 3, and 4.
The upper nuclear trigram consists of the lines in places 3, 4, and 5.
 Nuclear Hexagram
Nuclear Hexagram
These trigrams overlap each other and bring special emphasis to each place or line in the hexagram. The nuclear trigrams are then placed above each other to make a nuclear hexagram. Each nuclear hexagram will have an influence within four primary hexagrams. There are only sixteen hexagrams that can be nuclear hexagrams.
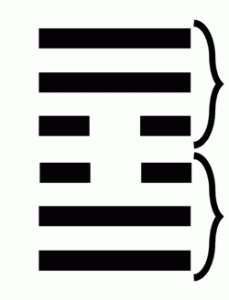
The Six Places
Each place in a hexagram has its own elevation and subsequent importance, being lower or higher, or inner and outer.
Places 1, 2 + 3 being inner or lower places.
Places 4, 5 + 6 being outer or higher places.
The primary and nuclear trigrams give special emphasis and influence on each place (line) of the hexagram.
The first place is only affected by one trigram.
It contains the 1st line of the lower primary trigram.
The second place is affected by two trigrams.
It contains the 2nd line of the lower primary trigram,
And it contains the 1st line of the lower nuclear trigram.
The third place is affected by three trigrams.
It contains the 3rd line of the lower primary trigram,
The 2nd line of the lower nuclear trigram,
And it contains the 1st line of the upper nuclear trigram.
The fourth place is affected by three trigrams.
It contains the bottom (1st) line of the upper primary trigram,
The top line of the lower nuclear trigram,
And the middle line of the upper nuclear trigram.
The fifth place is affected by two trigrams.
It contains the middle line of the upper primary trigram,
And the top line of the upper nuclear trigram.
The sixth place is affected by one trigram.
It contains the top line of the upper primary trigram.
Astrological consideration of the places:
The places of each hexagram correspond to the degrees of the zodiac.
Each place has a unique position as a degree in the 360 degree circle of the zodiac.
Twenty-four places share a degree, or there are twenty-four neutral places.
This allows for an exact correspondence of a line of the hexagram to a degree of the zodiac.
Further Considerations of the Places:
There are three powers.
What is above us.
What is below us.
And what we are doing in between.
These are seen first within each trigram. Each line represents one of these powers which can be active or passive.
In considering the entire hexagram, there is a doubling effect.
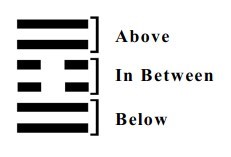
The upper two places represent what is above us.
The lower two places represent what is below us.
The middle two places represent what is between above and below.
Taken together there are four situations of the heavens or sky above us (over our heads).

The dark half The light half The light half The dark half
of morning of morning of afternoon of afternoon
The two lower places (1 + 2) represent what is below us or beneath our feet.

Beginning Maximum Beginning Maximum
firmness firmness to yield yielding
The two middle places (3+4) represent us in between. There are four types of human behaviour here.

Beginning Maximum Beginning Maximum
creative creative receptive receptive
Place Assessments
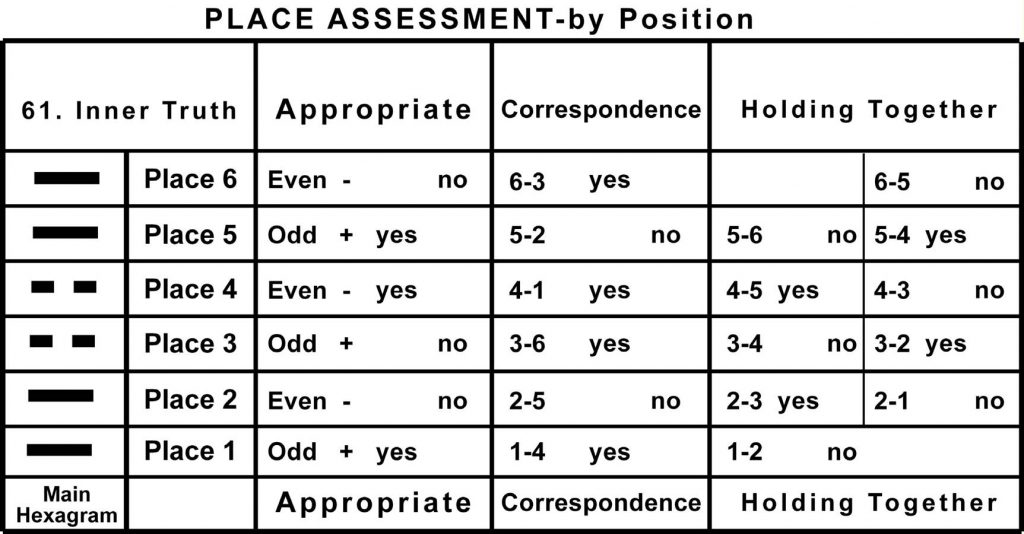
Appropriate:
When a solid (odd) line is in an odd place, it is appropriate.
When a broken (even) line is in an even place, it is appropriate.
When a solid (odd) line is in an even place, it is inappropriate.
When a broken (even) line is in an odd place, it is inappropriate.
Correspondence:
Two lines are said to be in correspondence when they are both in the same line of their respective trigrams and one is solid and the other broken.
Correspondence can happen between lines 1 and 4, 2 and 5, and 3 and 6.
Holding Together:
When a solid line is above or below a broken line they hold together and reinforce each other. (Note: In this text any two lines can hold together!)
